“费城杀手”:无处不在的环境细菌——嗜肺军团菌的出现

1976 年 7 月,正是酷热难耐、空调全速运转的季节,数百名“美国退伍军人联盟”的成员聚集在美国宾夕法尼亚州费城的贝尔维尤·斯特拉福(Bellevue Stratford)酒店召开大会(见图 1)。大会结束之后,周边城市接连几天突发重症肺炎传染病:147 名退伍军人联盟成员被送往医院,29 人(16%)死亡,但是并未发现任何常见的病因。在亚特兰大疾病控制与预防中心(CDCP)的支持下,警方开始展开调查,目的是找出“杀手”:几个月来“杀手”一直不为人知。事实上,它是一种对人类有害的新型细菌,后来被命名为“嗜肺军团菌”(Legionella pneumophila),其生存环境是淡水。一种新的环境源性疾病由此诞生了:军团病!
1. 50年前:军团病的出现

[资料来源:杰克·E·布彻, HABS 拍摄(公共领域)]
两篇基础性文章描述了这种“新”人类病原体的发现过程及其引发致命肺炎疫情的情况。1977年12月1日,也就是事件发生一年半以后, 弗雷泽等人[1]和麦克达德等人[2]分别在著名的医学期刊《新英格兰医学杂志》上发表了关于肺炎疫情的描述和病原检测的诊断方法。相关研究是由美国联邦机构 CDC[3]发起的。该机构拥有强大的科学、技术和财政资源,其唯一目标就是找出美国媒体口中的“费城杀手”!
疫情发生后,在众多微生物学家、化学家和毒理学家的支持下,大约 50 名来自流行病情报服务处(EIS)的流行病学家被部署到宾夕法尼亚州(图 2)。然而,所有已知病原体的研究都是阴性的。六个月后,麦克达德又重新采用罗伯特·科赫(Robert Koch) 技术,将已故患者的肺组织活检切片接种到豚鼠身上,然后在胚胎鸡蛋上进行亚种培养,最终观察到了细菌形态!在随后的一年中,疾病的主要特征和引发感染的病原体被确定下来:“由难以培养的革兰氏阴性杆菌引起的肺炎,最常见于高危人群(年长者、吸烟者),死亡率为10%,通过呼吸道进入,可能传播原因:空调系统”。全世界的媒体都广泛进行了报道,鲍勃·迪伦的歌曲《军团病》也使这一流行病“名垂千古”!

[资料来源:©J. Croizé的个人作品]
人们几乎是偶然情况下发现了军团菌,1981 年以此发现为主题的书作《创伤》[4]问世,该书引人入胜,读起来就像一部惊险小说。作者托马斯和 摩根-威茨 讲述了如何通过追踪患者、调查人员、医生和政客,提出最奇特的假设(禽流感、瘟疫、恐怖袭击、化学制剂、毒素等)并最终找到解决方案。迄今为止,经过半个世纪的传染性病原体的基础研究和临床病例的流行病学分析,我们在理解、诊断和预防军团病方面取得了巨大进展。尽管如此,这种疾病仍然是一个非常现实的问题,尤其是在法国(2018 年有 2133 例患者)。因为它的严重性以及它在社区获得性肺炎(仅次于肺炎球菌)中所占的比例很高。
2. “致命细菌”嗜肺军团菌的身份证
2.1. 什么是嗜肺军团菌
[资料来源:CDC-PHIL(公共领域)]
第一篇关于军团菌分类学[2]的开创性文章发表于1979年[5]。这是一种小型需氧革兰氏阴性菌[3],揭示了一个新的菌科——军团菌(以首批患者命名),军团菌科只有一个属(图3)——军团菌属。第一个被命名的菌种是嗜肺军团菌(Legionella pneumophila)(Philein:喜爱;Pneuma:呼吸),以提醒人们它所引发的疾病:肺炎,到目前为止,人们已经描述了65 种军团杆菌,其中只有大约20种是在人类和环境中共同发现的。一个显著的现象是其热耐受性强。这种细菌在25 °C到45°C的温度范围内繁殖。它可以在高达60°C的温度下存活,但在70°C以上时就会死亡。
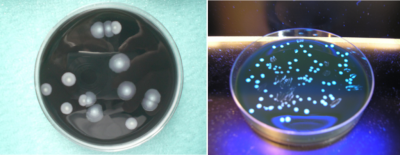
最初,无法在现有的培养基上繁殖军团菌。1979 年,开发出一种新型的特定培养基,这种培养基如今仍然适用。细菌分裂时间平均为4小时;一方面,它解释了菌落出现在培养物中所需的时间,需要2到5天(图 4),另一方面,解释了疾病的潜伏期在4 到10 天。识别菌落的几种方法是可行的:以前的生化技术很快被放弃,现在常规使用的是凝集试验的免疫学测试或质谱技术(MALDI- TOF-MS[4],[6])。
(右)。
[资料来源:© J.Croizé]
今天,人们已经描述的军团菌已不再是一种,而是 65 种,其中,最常见和最具致病性的是人类嗜肺军团菌血清1型。其致病性主要是由于存在大量参与细胞内增殖的因子,包括巨噬细胞感染增强因子(MIP)和三种分泌系统,其中最重要的是IV型分泌系统[7]。在已测序的菌株中,嗜肺军团菌巴黎型和嗜肺军团菌Lens型 显示出有370 万个碱基对(Mbp)的基因组。分析特别表明,存在与两个已知宿主(自由生活的阿米巴[5]和人类)具有同源性的蛋白质编码基因。随后,人们对来自不同宿主的同源蛋白进行了表征,解释了这种微生物的适应能力[8],特别是对人类最致病的物种:血清1型 嗜肺军团菌的适应能力。
2.2. 嗜肺军团菌的生物群落是什么?

[资料来源:© J.Croizé]
军团菌的自然栖息地是各种各样的淡水:湖泊、河流、池塘(图 5)和温泉。它们在海水中不存在[9],[10]。这种水生和大地水生[6]细菌可以以三种不同的形式存在于自然界中:
- 在自由生活的阿米巴中:这种非寄生的原生生物[7]完全在环境中完成其生命周期,在水中通过吞噬微生物(包括军团菌)为食。但是,军团菌对阿米巴也有一种自然的“抵抗力”;它们将自己内化在一个名为含军团菌的液泡(LCV)中,该液泡构成了环境中优先繁殖的场所;因此,军团菌能够“藏匿”在阿米巴中并抵抗环境压力(图 6)[11]。这些真核生物(棘阿米巴属、哈特曼氏菌属等)因此成为潜在的污染源。
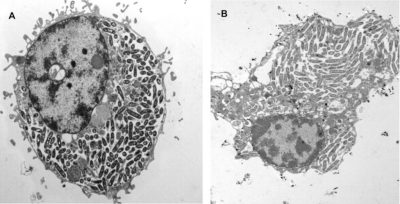
多噬棘阿米巴(B)在 感染嗜肺军团菌(AA100 菌株)24小时后的电子显微镜照片。图片来自 Molmeret 等人(见参考文献[11]),经美国微生物学会授权。
- 在细菌生物膜[8],[12]中:生物膜(参见细菌生物膜和健康)由围绕在细胞外基质中的微生物和附着在物理化学表面的动态环境组成,该模式适用于军团菌。但是,生物膜也可以在静止的液体介质表面或“浮动生物膜”上找到:它们对细菌的持久生存起着至关重要的作用,水体中的细菌因为这种生物膜而不能触达,甚至很难用消毒剂彻底根除。

[资料来源:© J.Croizé]
- 以可存活但不可培养的细菌(VBNC)[13]的形式出现:这些细菌在受到压力的影响下出现,由于代谢活性较低低而使它们暂时无法繁殖。然而,如果条件再次变得有利,它们可以恢复其致病能力。
人工或人造的栖息地:空气冷却塔(图7)和生活热水(DHW)装置[14]、[15]。军团菌可以从自然栖息地移居到人造栖息地,并在温度允许的情况下(25 到 45°C)繁殖。因此,任何包含热水的设备或网络都将构成军团菌的潜在生态位。从历史上看,空调系统、冷却塔和蒸发式冷凝器也被指责为罪魁祸首:这就是“空调”一词总是与“军团病”紧密相连的原因!后来证明,所有“现代”的家用热水网络都有可能被军团菌占领,并且在一些区域风险更高,例如淋浴、按摩浴缸、装饰性喷泉等。
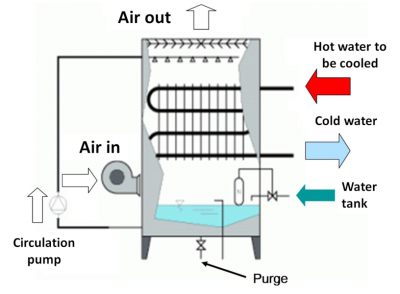
[资料来源:KW (CC BY-SA)
- 空气冷却塔是第一个与疫情爆发直接相关的装置。工业热回路或用于空调的制冷设备(工业、商业)有利于军团菌的繁殖(装置中的水温和空气/水接触)。位于建筑物外的湿式冷却塔是这些热回路的冷却系统,会产生由细小水滴组成的气溶胶,这些水滴从通风口排出。风险的程度或大或小取决于周围人口的位置和密度。例子比比皆是,比如高尔夫球手所在的公共汽车站位于落尘下,球手被动吸入了建筑物本身或邻近建筑物释放的蒸气。涉及工业冷却塔的风险较少。但1997年在朗斯爆发的疫情显示,被感染的患者居住在离冷却塔8公里甚至 16 公里的地方(图 8)!

[资料来源:Tanakawho (CC BY 2.0)]
- 生活热水(图 9 和图 10)最初是供家庭使用的冷水,然后会被加热。这是苏珊·费舍尔-霍克(Susan Fisher-Hoch)在英国观察到的易污染区域,在英国人们很少用空调[16]。水通过不同装置进行加热,这些加热装置可以是个人的,也可以是集体的,比如锅炉、热水器等,然后通过较长的供水管道输送到家庭的汲水点(水龙头、淋浴),变成生活热水。
军团菌可能以非常低的浓度存在于冷水中,如果温度条件允许,可以在其中进行繁殖。受污染的热水在转化为气溶胶时会变得危险:例如,淋浴、水疗、喷雾、装饰性喷泉,甚至是洗车设备和牙科用的水枪都是这种情况。

医院的污染风险与外部是相同的,但因其接纳许多因病(免疫抑制)或治疗(皮质类固醇治疗)而身体虚弱的患者,污染的风险大大增加。2001 年乔治·蓬皮杜欧洲医院开业时发生的军团菌病流行仍然是一个经典的案例,提醒人们供水管道设计的重要性以及关注供水管道水停滞时间的重要性。
其他栖息地要少得多,其中有类似“盆栽用土”的潮湿土壤,其中的肥料可能被特殊的长滩军团菌( L.longbeachae) 污染,长滩军团菌也可引起人类疾病。
2.3. 细菌是如何进入人体的?
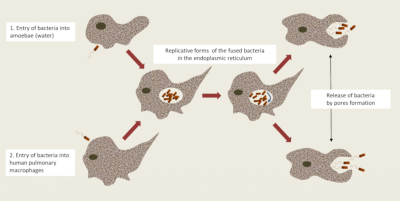
(译者注:1.entry of bacteria into amoebae(water) 1.细菌进入阿米巴(水);2.entry of bacteria into human pulmonary macrophages 2.细菌进入人肺巨噬细胞;replicative forms of the fused bacteria in the endoplasmic reticulum 融合细菌在内质网中的复制形式;release of bacteria by pores formation 细菌在孔隙形成过程中的释放)
现在已经证明,人类通过吸入被军团菌污染的热水气溶胶而感染:这些气溶胶中包含着直径小于5 µm但大到足以容纳细菌的飞沫(直径大于2 µm)[17]。任何健康的人暴露在微生物环境中通常都能够通过肺部的巨噬细胞来保护自己,这些巨噬细胞是被称为“肺部清洁工”,它们能摧毁已摄入的微生物。但如果存在吞噬异常,或者感染的菌株具有特殊的毒力,或者细菌浓度很高,那么巨噬细胞就会变为“意外宿主”。军团菌在吞噬溶酶体液泡(LCV)中繁殖,就像在阿米巴中一样,然后带着增强的毒力逃逸出来(细菌重新变成鞭毛形态)。这一过程主要见于嗜肺军团菌,该种属占所有军团菌病病例的90%以上(图 11)。该细菌被归类为细胞内繁殖细菌,需要使用能够在细胞内扩散的抗生素来治疗。
这些特点意味着军团病不是人传人的疾病(仅在2016 年葡萄牙公布了一个例外),而是一种机会性疾病,其发生很大程度上取决于个人风险因素!
2.4. 什么是军团菌病?
军团病是一种肺炎[17],其平均潜伏期为接触污染源后5天;感染剂量为每升1000CFU(菌落形成单位)嗜肺军团菌。某些人群比其他人群更“高风险”(即使在20%到30%的案例中没有检测到任何风险因素)。目前已确认的促成因素由三个:
- 年龄大于50 岁(军团菌病在儿童和20岁以下的年轻人中很少见);
- 吸烟者(45% 的病例);
- 男性(75% 的病例)。
其他免疫系统较弱(恶性血液病、癌症、免疫抑制治疗、长期皮质类固醇治疗)。 甚至是有慢性心脏或肺部疾病、糖尿病的患者,需要采取严格和规范的的预防和监测措施,特别是在生活热水(DHW)中强制执行“零军团菌”标准。
[资料来源:© J Croizé]
临床上,军团病存在两种形式:庞蒂亚克热(类似流感样症状,不伴有肺炎,不治疗的情况下可在2 到5天内自愈,潜伏期几小时到48 小时)。军团病是一种严重的临床和放射学肺炎,呈现类似流感的症状,没有特异性体征。在没有治疗的情况下,死亡率为10% 。可严格按照美国国家药品和健康产品安全局(ANSM)的建议开具适当的抗生素进行治疗(如细胞内抗生素,包括大环内酯类、氟喹诺酮类或利福平)。考虑到感染的严重性,抗生素治疗可在一个月内治愈。
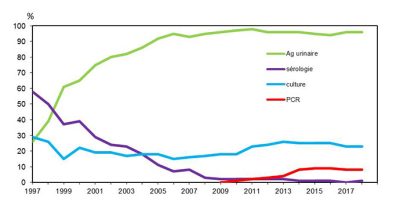
军团菌病是一种严重的疾病,因此准确诊断对于治疗目的和监测目标都很重要。诊断需要结合肺部疾病的情况以及以下4 项微生物标准中至少一个阳性结果[19](图 12):
-
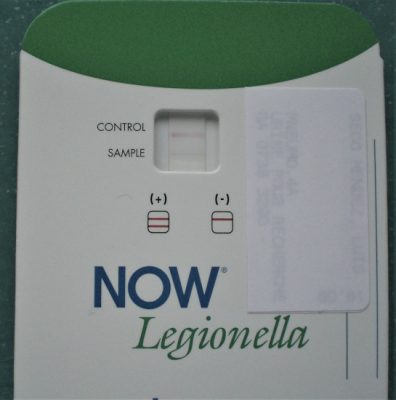
- 军团菌尿液抗原监测测试(Now Legionella)中存在军团菌可溶性抗原(图 13);
- 使用PCR 技术直接在支气管-肺部样本中寻找DNA ;
- 从肺部样本(痰液或支气管肺泡灌洗液)中通过培养分离出细菌,然后对分离的菌株进行分型;
- 通过证明血清转化来提供事后确认。
3. 在法国和欧洲,如今人们对军团菌病的流行病学有哪些了解?
流行病学是医学的一个分支。它研究一种疾病在大量个体中的发生率和流行率,并检测流行病的源头和致病因素。
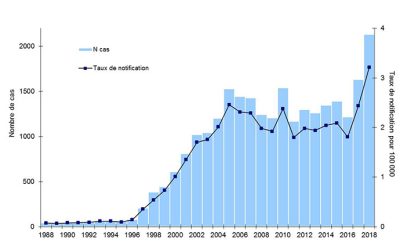
[资料来源:经法国公共卫生局数据中心(Données de Santé Publique France)许可转载(见参考文献[19])]
(译者注:nombre de cas 病例数;taux de notification pour 100000 每十万人的发病率;N cas N 个病例;Taux de notification 发病率)
对军团菌病爆发的流行病学调查被认为具有根本重要性。作为一个公共卫生问题,军团病被列入必须申报和通知的强制申报疾病名录(1987)。法国的监控系统行之有效(图14),既有可靠的诊断测试(尿液中可溶性抗原检测——1997 年),又规定必须将分离的菌株发送至里昂的国家军团菌样本中心(Centre National de Référence des Legionelles)[20]。监测系统是基于对从军团菌和环境中分离出的菌株研究而建立的。
如今进行了不同类型的分析,实现了对军团病流行病学的可靠描述:
- 根据监管机构定义的标准,参照生物检测结果,可将军团病病例记录和分类为“确诊”或“可能”;
- 根据疾病获得的地点将其分类为“医院[10]获得性病例”或“社区获得性病例”;
- 根据相同菌株影响的人数记录疾病的传播情况:孤立病例、群体病例或流行病例(见表1);
- 在法国以外的其他国家旅行有关的病例在欧洲军团菌监测网络 EldsNet[21]进行报告。
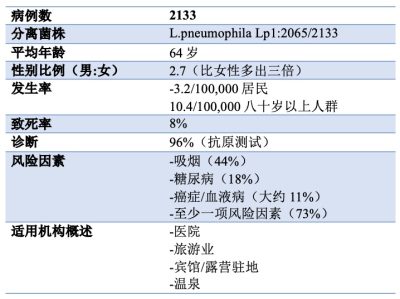
表1. 2018 年军团菌病病例流行病学数据,摘自2019年法国公共卫生局数据中心(Données de Santé Publique France 2019)(见参考文献[19])
从 2018 年法国军团病流行收集的数据(2019年8月公布的数据)揭示了表 1 中总结的特点;在其评论中,法国公共卫生局[22]强调了明显增加的是病患总数为2,133 例和 全国发病率为3.2% ,这是自 1988 年开始监测以来记录的最高数字。
但是并没有发现特别的原因,除了6 月份病例明显增加(气象条件有利)和许多零星病例,并没有出现新的危险因素。
在欧洲,由欧洲疾病预防和控制中心(ECDC)负责病例的通报。这一监测在三十个欧洲国家有效执行。报告病例数从2013 年的 5,835 例增加到 2017 年的9,238 例[23]。发病率为每10万居民1.8例。
报告军团菌病病例最多的四个国家分别是:第一意大利:2013 例;第二法国:1,630 例;第三西班牙:1,363 例;第四德国:1,280 例。但应谨慎对待这些数字,因为并非所有国家/地区都拥有最新的诊断手段。然而,使用的测试手段和监测系统对于数据是否准确非常重要。
值得注意的是,美国 2014 年的年发病率为每10 万居民1.62 例,自2000 年( 0.42 例)以来一直在增加。
4. 是否可以预防军团菌病?
4.1. 我们如何监测水质系统?
军团病是无法接种疫苗预防的!因此,所有的预防策略都依赖个人或集体所采取的措施。
针对生活热水和冷却塔系统的预防措施基于若干基本法规文件[24]:公共卫生高级委员会于2013 年 7 月 11 日发布的调查指南和管理帮助、2010 年 2 月 1 日法令、2010年12 月23日通告、2010 年12 月14 日法令、2013年12月14 日法令。
生活热水使用的一般规范(参见法兰西岛地区卫生局发布的监测表):
无论是个人使用还是集体使用,都必须持续控制热水储水箱的温度,其应为:
- 烧水温度高于55°C;
- 出水温度高于50°C;
- 冷水的温度应低于20°C。
必须定期对热水设备进行维护和监控:清除管道中的积水、检查管道是否存在腐蚀、为水龙头和淋浴喷头除垢以及纠正供水网络的不良维护等。
个人预防“在家中”。除了上述规则外,还有两个重要的预防措施:
- 长时间不在家后(假期后),必须给所有热水龙头和淋浴喷头放水几分钟。
- 注意很少使用的供水点,这是军团菌潜在的储存库。
根据人类活动将风险分为两组:
A 组:具有高度军团菌扩散风险的设施:
- A1:在一个或多个市镇范围内(数平方百米或数平方公里)。安装在建筑物屋顶或工业场所用于冷却空气的冷却塔。污染是由热水蒸气释放到大气中造成的。为防止此类污染,必须定期使用生物杀菌剂对冷却塔进行维护、清洁和消毒。
- A2:公共水源周围几平方米:集体生活热水系统。
B组:
- B1:集体水雾化设备、水疗中心、洗车机、污水处理厂的泻湖系统、专业高压水清洗设备。
- B2:用于氧疗、睡眠呼吸暂停、药物雾化、牙科护理中使用的设备。
4.2. 如何知道供水系统被污染了?
水监测方法由法国标准化协会(AFNOR) 发布的NF T 90-431条款严格规定, 条款名称为“水质-军团菌属和嗜肺军团菌的检测和计数”。这是一种通过直接接种和浓缩后的方法。它适用于所有类型的水:干净水和脏水。自2010 年起,采用分子生物学型PCR技术的NF T90-471 标准已经存在:该技术是在卫生部门特别要求下执行的。
4.3. 公共接待场所有哪些义务?
对于这些常说,必须执行2010 年2月1日的法令和2010 年12月21日的通告(参见参考文献[19]),以防止生活热水系统受到污染。它们涉及在卫生机构、医疗机构、医疗社会机构以及监狱、酒店和旅游住宿、露营地和其他向公众开放的场所中生活热水生产、储存和供应的设施中的军团菌监测。
可在互联网上查阅的其他相关文件,专门适用于从露营地到酒店的所有类型的公众接待场所:
- 水疗中心和游泳池的军团菌监测,温泉军团菌监测,
- 汽车清洗设备军团菌监测,
- 旅游设施的军团菌监测,
- 旅游场所的军团菌监测,
- 冷却塔军团菌监测(2014年1月20日),
- 对住宅建筑的建议。
关于医院,法国卫生部医疗健康司和法国卫生高级委员会的通告帮助医疗保健专业人员了解住院患者所面临的风险,并制定了指南。现实当中,医院内获得性感染控制委员会(CLIN)和卫生部门已制定程序,包括设计“水质监测手册”[25]。
4.4. 遇到污染时应该怎么办?

(译者注:risques legionelles 军团病风险;alerte 警告;measures d’urgence en presence de legionelles 出现军团病应采取紧急措施)
如果供水管网被军团菌污染,管理者必须立即根据风险级别采取适当的措施[26]。如果是医疗机构或养老院,将立即采取纠正措施:停止使用水和/或在水龙头和淋浴上安装一次性过滤器,以阻止所有大于0.2微米的颗粒(2002年4月22日和2005年10月28日的通告)。
在进行简单消毒时,可采取多种处理措施,使用一种方法或多种方法。可以是:
- 机械方法:管道除垢或修复;
- 物理方法:特别是热冲击。仅用于热水管网,包括将水温保持在 70°C 至少 30 分钟。这种方法已在中等规模的医院中使用,但它需要在加热过程中完全停止用水,并且在每个使用点都需要有工作人员在场,以避免烫伤他人;或者
- 化学方法:使用高度受控的化学试剂,其中主要是产生次氯酸盐的氯化物。
5. 谨记
- 在 20 世纪 70 年代和 80 年代,出现了三种主要的细菌性传染病:(1)引发莱姆病的伯氏疏螺旋体,(2)导致胃溃疡的幽门螺杆菌和(3)引起军团病的嗜肺军团菌。
- 每一次,致病细菌都是在偶然的机会中发现的。事实上,它们早已存在,只是一直为被人所知!
- 军团菌肯定早在费城疫情爆发之前就存在于环境水体中,但由于它们还没有机会感染人类,所以它们并不为人所知。
- 人类为了舒适、消遣或满足工业用途在各种不同场景下使用热水,从而导致了一种全新的、完全无法预测的风险。
- 因为军团菌在淡水环境中无处不在,所以在环境中根除它是不可能的。
- 我们所有人的责任是推广和执行正确使用热水的严格规定,防止其发生污染。这些规则首先必须付诸实施以保护处于“高风险”人群。
感谢 Krysha Marca 夫人在将法文原文译成英文方面提供的宝贵帮助。
参考资料及说明
封面图片:有关军团病报刊杂志照片的拼图。
[1] Fraser DW, Tsai TR, Orenstein W. et al Legionnaires’ disease: description of an epidemic of pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med.1977, 297, 1189-1197
[2] McDade JE, Shepard CC, Fraser DW et al. Legionnaires’ disease. Isolation of a bacterium and demonstration of its role in other respiratory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1977, 297, 1197-1203
[3] https://www.cdc.gov/
[4] Thomas G. & Morgan-Witts M., Trauma – The search for the cause of Legionnaires’ disease. Arrow Books, 1981; Thomas G. & Morgan-Witts M., Trauma – In search of a murderous virus, French translation by Destanque P., Ed. Encre 1982
[5] Brenner DJ, Steigerwalt A.G. McDade J.E. Classification of the Legionnaires’ Disease bacterium: Legionella pneumophila, genus novum, species nova of the family Legionellaceae, familia nova. Ann. Intern. Med. 1979, 90, 656-658.
[6] Moliner C., Ginevra C., Jarraud S. et al. Rapid identification of Legionella species by mass spectrometry. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59,273-284;
[7] Mish EA. Legionella: virulence factors and host response. Curr. Opinions. Infect. Dis. 2016, 29, 280-286
[8] Gomez-Valero L., Rusniok C., Carson D. et al. More than 18,000 effectors in the Legionella genus genus provide multiple, independent combinations for replication in human cells. Process Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 116 (6) 2265-2273; first published January 18, 2019 https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1808016116
[9] Fliermans C.B., Cherry W.B., Orisson L.H., Smith S.J., et al. Ecological distribution of Legionella pneumophila. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 1981, 41, 9-16
[10] Orisson L.H., Cherry W.B., Fliermans C.B. et al. Characteristics of environmental isolates of Legionella pneumophila. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 1981, 42, 109-115
[11] Molmeret M. et al. Amaoebae as training grounds for intracellular bacterial pathogens. Appl. About. Microbiol. 2005; doi:10.1128/AEM.71.1.1.20-28.2005
[12] Lau H.Y. &Ashbolt N.J. The role of biofilm and protozoa in Legionella pathogenesis: implications for drinking water. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009,107,368-378; Steinert M., Hentschel U.& Hacker J. Legionella pneumophila: an aquatic microbe goes astray. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 26, 149-162; Declerck P. Biofilms: the environmental playground of Legionella pneumophila. Env.Microbiol.2010, 12, 557-566; Abdl-Nour, Duncan C, Low D.E et al . Biofilms: the stronghold of Legionella pneumophila. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21660-21675
[13] Dietersdorfer E., Kirschner A., Schrammel B. et al Starved viable but non-culturable (VBNC) Legionella can infect and replicate in amoebae and human macrophages. Water Res. 2018
[14] Fields B.S., Benson R.F. & Besser R.E. Legionella and Legionnaires’ Disease: 25 years of investigation. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 13, 506-526
[15] Cunha B.A., Burillo A.&Bouza E. Legionnaires’ disease. Lancet 2016, 387, 376-385
[16] McCormick J.B. & Fisher-Hoch S. 1997. Chasseurs de virus. Presses de la Cité, 498 pages
[17] Jarraud S., Reyrole M., Meugnier H. et al Légionellose. Presse Med 2007, 36, 279-87; Jamilloud Y., Jarraud S., Lina G., et al. Legionella, legionellosis, 2012, Med Sci (Paris) 28, 639-45
[18] ANSM:国家药品和健康产品安全局(取代 AFSSAPS),一个法国机构
[19] 2018 年法国军团病病例报告( 2019年8 月) 法国公共卫生署. Santé Publique France. https://www.santepubliquefrance.fr/maladies-et-traumatismes/maladies-et-infections respiratoires/legionellose/articles/bilan-des-cas-de-(in french)
[20] 法国国家军团菌样本中心。 http://cnr-legionelles.univ-lyon1.fr/
[21] ELDSNet:欧洲军团病监测网络,由 ECDC(欧洲疾病预防控制中心)协调,创建于 2005 年。 EWGLI(欧洲军团菌感染工作组)创建于 1986 年,后来成为 EWGLINET,然后在2010 年再次更名为 ELDSNet。
[22] 法国公共卫生署。自2016年5月1日起,它合并了以下机构:国家卫生监测研究所(INVS)、国家健康预防与教育研究所(Inpes),卫生紧急情况准备与响应机构(Eprus)。
[23] European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, Legionnaires’ disease. In: ECDC. Annual epidemiological report for 2017 (2019), Stockholm.
[24] https://www.hcsp.fr notices and reports/guide for investigation and case management assistance in legionellosis, https://www.iledefrance.ars.sante.fr/la-legionellose (in french)
[25] Cheron J. (2006) Maîtriser le risque légionelles. Ed. Johanet, 325 p. (in french)
[26] 军团菌病的预防:按安装和设施类型划分的责任
环境百科全书由环境和能源百科全书协会出版 (www.a3e.fr),该协会与格勒诺布尔阿尔卑斯大学和格勒诺布尔INP有合同关系,并由法国科学院赞助。
引用这篇文章: CROIZE Jacques (2024年3月10日), “费城杀手”:无处不在的环境细菌——嗜肺军团菌的出现, 环境百科全书,咨询于 2024年7月27日 [在线ISSN 2555-0950]网址: https://www.encyclopedie-environnement.org/zh/sante-zh/%e8%b4%b9%e5%9f%8e%e6%9d%80%e6%89%8b%ef%bc%9a%e5%97%9c%e8%82%ba%e5%86%9b%e5%9b%a2%e8%8f%8c%e7%9a%84%e5%87%ba%e7%8e%b0-%e4%b8%80%e7%a7%8d%e6%97%a0%e5%a4%84%e4%b8%8d/.
环境百科全书中的文章是根据知识共享BY-NC-SA许可条款提供的,该许可授权复制的条件是:引用来源,不作商业使用,共享相同的初始条件,并且在每次重复使用或分发时复制知识共享BY-NC-SA许可声明。